The Essential Guide to Omega-3s: Why DHA is the Ultimate Brain-Boosting Nutrient
Note: DHA and DHEA, despite being similar acronyms, are two different things entirely. This article discusses DHA or docosahexaenoic acid, an omega-3 fatty acid derived from food sources. DHEA is dehydroepiandrosterone, which is a synthetic hormone. While synthetic hormones may have beneficial uses in some cases, they are not discussed here a nutrition for optimal brain function and repair. That being said, let's talk about the food derived omega-3 fatty acid known as DHA.
If you want to improve brain function, support mental clarity, and optimize long-term cognitive health, then Omega-3 fatty acids—especially DHA (docosahexaenoic acid)—should be at the top of your list.
These healthy fats are critical for reducing inflammation, improving memory, supporting focus, and even promoting emotional well-being. They play a key role in brain plasticity—our brain’s ability to adapt, heal, and grow throughout life.
Whether you’re looking to enhance your cognitive performance, support brain recovery, or protect against age-related decline, DHA is the ultimate nutrient for brain optimization.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Why Do They Matter?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats, meaning the body cannot produce them on its own—we have to get them from food or supplements. There are three main types of Omega-3s:
- ALA (Alpha-linolenic acid) – Found in flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic acid) – Found in fatty fish and known for its powerful anti-inflammatory effects.
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic acid) – The most important Omega-3 for brain health, also found in fatty fish.
Although ALA can be converted into EPA and DHA, the conversion rate is shockingly low. Studies show that only 10% of ALA converts to EPA, and less than 1% becomes DHA.
For this reason, relying on plant-based Omega-3 sources alone is not enough for optimal brain health—we need to get DHA directly from fish, seafood, or high-quality supplements.
Why is DHA the Most Important Omega-3?
DHA is the rarest and most essential Omega-3 fatty acid for the brain. It’s a core structural component of brain cells, making up about 30% of brain matter and 50% of the retina in our eyes.
This means that without enough DHA, your brain can’t function at its best.

DHA and Brain Protection
Research shows that DHA provides the strongest neuroprotective effects compared to other Omega-3s:
- The Chicago Study found that DHA had a significant impact on memory and brain health, even more than EPA (1).
- People with low DHA levels in the hippocampus (the memory center of the brain) have been linked to Alzheimer’s disease (2,3).
- The Rotterdam Study found that eating just one serving of fatty fish per week reduced cognitive decline and dementia risk by up to 60% (4).
Even in young, healthy individuals, DHA improves learning, memory, and focus (5,6).
DHA’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties also help protect brain cells from oxidative stress and aging.

How Omega-3 Imbalance is Hurting Your Brain
One major issue today is that most people consume way too much Omega-6 and not enough Omega-3s.
The ideal Omega-3 to Omega-6 ratio is 1:1 or 1:2. However, in the U.S., the average person eats an imbalanced ratio of 1:16 to 1:36—a recipe for chronic inflammation, brain fog, and long-term health problems.
The biggest culprits? Processed foods, vegetable oils, and fried foods loaded with inflammatory Omega-6s, including:
- Canola oil
- Soybean oil
- Corn oil
- Cottonseed oil
- Margarine & processed foods
To restore balance, it’s critical to increase DHA intake while cutting back on processed and fried foods.
How Much DHA Do You Need?
The American Heart Association recommends at least two servings (3.5 oz.) of fatty fish per week for heart and brain health. But most people don’t meet this requirement.
Most Western diets provide only 100-200 mg of EPA/DHA per day, whereas experts recommend at least 650 mg daily for optimal health.
For brain recovery, inflammation, or cognitive enhancement, 1,400 mg or more per day may be ideal.
Good news: DHA is very safe, and the FDA considers doses up to 5 grams per day safe for adults.
What About in Children?
The next crucial piece of this omega-3 puzzle lies in fetal brain development and the first few years of our lives which are some of the most formative years for our brains and neurons.
I have often stated the importance of healthy fats because our brains are about 60% fat. I also like to remind everyone that our brains consume about 25% of our total energy and nutrition even though our brains make up only a small part of our body mass.
When we are in the womb, this energy consumption goes up to 70%! Almost all of our energy resources go to building our brain and nervous system when we are a fetus. Evidently, DHA is a crucial part of this building process.
Our Brain and Our Eyes
DHA makes up about 30% of our brain matter and approximately 50% of the retinal structure in our eyes. Adding DHA to your diet not only increases cognitive function, but it also increased visual acuity in developing humans and animals (7).
This alone should enough of a reason to make sure you are getting enough DHA in your diet. However, another study found that babies born with neurological problems had low levels of DHA, had elevated levels of trans fats in their brains (8).
Avoid Trans Fats and Get DHA
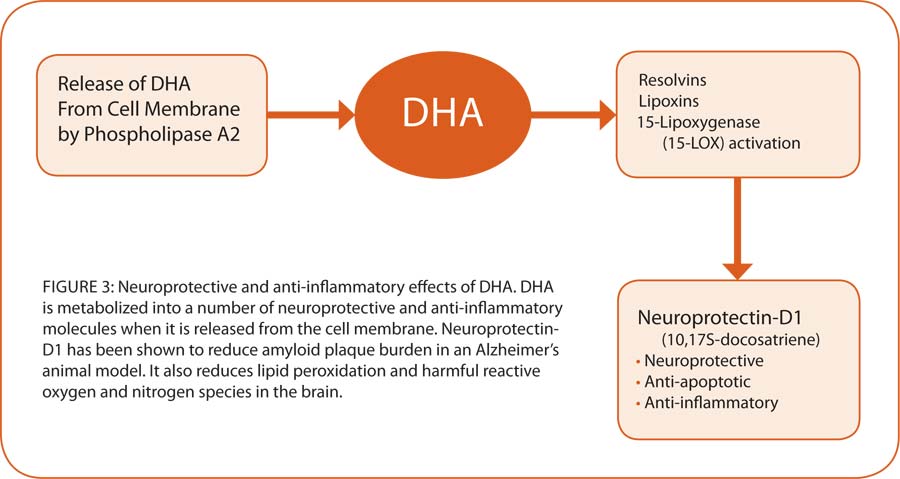
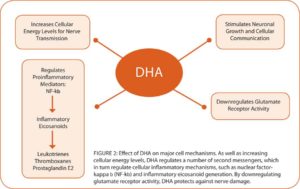
DHA reduces inflammation by reducing the expression of Nf-kB (Nuclear factor kappa-beta) among many other anti-inflammatory actions shown in the image below.
Nf-kB is an inflammatory marker in our bodies that we can measure that can generally show us how much inflammation or oxidative stress is occurring in our bodies.
An Imbalance of Fatty Acids
What’s scary is that we, in the United States, have an imbalance of fats in our diets that is disastrous! It is recommended that we eat a 1:1 ratio or at most a 1:2 ratio of omega-3 fatty acid to Omega-6 fatty acid.
However, the average American eats between 1:16 and 1:36 ratio of Omega-3 to Omega-6. Many of us are eating too many fried foods that are cooked in rancid (oxidized) Omega-6 oils like vegetable oil, canola oil, cottonseed oil, soybean oil, and other common polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA’s).
In order for our bodies to properly metabolize these fats, we need a balance of them in pretty even ratios.
Some oils like olive oil are naturally in a healthy balance of Omega-3 to Omega-6. However, other oils like vegetable oil and canola oil are almost entirely Omega-6 fatty acids.
How Much is Enough?
The American Heart Association says that we should eat two or more servings (3.5 oz.) of fatty fish like salmon, sardines, etc. This is in order to support cardiovascular health. However, a dietary survey of shows that most Americans eat half that amount or less.
According to one dietary study (9), most Americans get a dose of combined EPA and DHA equaling 100-200mg per day while many experts recommend getting at least 650mg (combined EPA/DHA) per day, and if you are not deficient or dealing with a traumatic brain injury, then 1,400 mg/day combined EPA and DHA should be plenty but bore can be even more beneficial. Especially if you are deficient.
And it’s hard to get too much. A report requested by the European Commission found that “supplemental intakes of EPA and DHA combined at doses up to 5 g/day… do not raise safety concerns for adults.” CITE
Introducing Feed a Brain Oil-Burn🔥Omega Monoglyceride Fish Oil

Since my severe TBI, I needed to support and protect the brain. So I research like my life depended on it… because it did. In my research, DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) is THE most powerful nutrient I have found to protect the brain from neurological damage and degeneration. It is also the most powerful nutrient for aiding in the restoration of brain function after neurological injury. This is why I have searched far and wide for the best supplements. By comparison, a concentrated DHA in monoglyceride form is what I have found to be the cream of the crop!
Why Monoglyceride?
The production of fish oil concentrates requires converting the fish oil into a form that can be encapsulated. There are typically two different forms of fish oil supplements:
- Ethyl Ester (EE): Using a chemical process called “molecular distillation”, the natural triglyceride form of a fish oil is broken apart and an ethanol molecule is attached to the free fatty acids created. This process allows for a “fish oil concentrate,” but these fish oils lack a glycerol backbone. Because of this the fatty acids are unstable and are looking for an available triglyceride backbone which they may take from an existing molecule in our brain or body. When this occurs, our cells are actually damaged. Additionally, studies have shown that ethyl esters are the least bio-available forms of omega-3’s.(8)
- Triglyceride (TG): Fish naturally contain the omega-3 fatty acids EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) as triglyceride esters. Evidence suggests that triglyceride (TG) fish oils are better absorbed in comparison to EEs. And because we can only use what we absorb, absorption is VERY important! So, because they are better absorbed (and because they aren’t creating a domino effect of unstable fatty acids in our bodies), TGs are better than EEs.
Monoglycerides are up to 3.5x better absorbed than triglyceride fish oils!
Our bodies enzymatically break down triglycerides into monoglycerides that we can then use. However, this monoglyceride Fish Oil is already enzymatically broken down into its high potency monoglyceride form. This makes Oil-Burn🔥Omega up to 3.5x more absorbable than an equivalent dose of ethyl ester fish oil!
This technology means that the DHA, sourced from cold water fatty fish, has already been pre-digested so that up to 3.5 times the DHA and EPA is able to be readily absorbed by our cells.
Studies conducted by the manufacturer of MaxSimil provide promising results suggesting better absorption than other fish oils. An unpublished, double-blind, crossover, pharmacokinetic study was performed in healthy overnight-fasted male and female subjects (N = 20) ages 19 to 60. Each subject was administered a single dose of six softgels (containing ~2000 mg EPA and ~1500 mg DHA) of either ethyl ester (EE) fish oil or MaxSimil. Compared to the EE form, MaxSimil EPA and DHA reached a peak concentration more than three times higher than that reached by EE fish oil. Moreover, MaxSimil not only reached maximum concentration faster but also maintained plasma levels longer.*[11-13]
Order Oil-Burn🔥Omega Monoglyceride Fish Oil Here
What About Vegan Sources?
ALA can be found in many vegetarian and vegan sources like flax, hemp, and chia seeds while EPA and DHA (the important conditionally essential fatty acids) are primarily found in animal foods like fatty fish and eggs.
If you are a vegan, then I highly recommend supplementing EPA and DHA. Luckily, there is one vegan source of EPA and DHA that is cold-pressed from algae. You can find our favorite vegan omega-3 supplement (including EPA and DHA) by clicking on the image below.
What If You Are Deficient in Omega-3’s?
Bear in mind that this recommendation is if you are healthy, and not deficient in Omega-3’s! You may require far more under certain circumstances.
In addition to supporting a healthy brain, Omega-3’s have also been shown to have beneficial effects on obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular health (10).
A National Health Crisis
When we combine all of this data, we can clearly see that EPA and DHA are much more essential than we once thought, and that most people in the U.S. are not getting enough which is leading to a lot of complications.
There was a study done at Harvard that was funded by the Center for Disease Control. It was estimated that approximately 96,000 deaths every year were caused by diseases related to omega-3 deficiency! These are mainly due to cardiovascular and neurodegenerative disease.

Food First, Supplement Second
In our opinion getting these nutrients from your diet is the best option because there are other amazing nutrients found wrapped up in food sources of Omega-3’s that you will not get with a supplement.
However, if you live on the go like most of us, or cannot eat fatty fish, and/or eggs for some reason, then we highly recommend getting a supplement just to cover all of your bases. Below are some of the suppliers we love for fish, and fish oil.
Vital Choice and JJ Virgin
We have taken great care to select only the highest quality fish products from pristine fisheries with very low contamination from toxins that are all too common in your average store bought fish.
We also choose companies that fish sustainably in order protect our environment from further degradation. All of the fish oils we recommend are molecularly distilled to remove neurotoxins like mercury. Also, they are held to international quality standards that are validated by third party laboratories.

Oil-Burn🔥Omega Monoglyceride Fish Oil
FDA Compliance
The information on this website has not been evaluated by the Food & Drug Administration or any other medical body. We do not aim to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any illness or disease. Information is shared for educational purposes only. You must consult your doctor before acting on any content on this website. Especially if you are pregnant, nursing, taking medication, or have a medical condition.
*The outcome of a systematic review and meta-analysis showed that although omega-3 supplementation does appear to improve childhood psychomotor and visual development, more studies are needed to confirm these conclusions and to explore the significance of IQ later in childhood.
Citations:
(1) Morris MC, Evans DA, Bienias JL, et al. Consumption of fish and omega-3 fatty acids and risk of incident Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2003 Jul;60(7):940-6.
(2) Soderberg M, Edlund C, Kristensson K, Dallner G. Fatty acid composition of brain phospholipids in aging and in Alzheimer’s disease. Lipids. 1991 Jun;26(6):421-5.
(3) Prasad MR, Lovell MA, Yatin M, Dhillon H, Markesbery WR. Regional membrane phospholipid alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Res. 1998 Jan;23(1):81-8.
(4) Kalmijn S, Launer LJ, Ott A, Witteman JC, Hofman A, Breteler MM. Dietary fat intake and the risk of incident dementia in the Rotterdam Study. Ann Neurol. 1997 Nov;42(5):776-82.
(5) Morris MC, Evans DA, Tangney CC, Bienias JL, Wilson RS. Fish consumption and cognitive decline with age in a large community study. Arch Neurol.2005 Dec;62(12):1849-53.
(6) Gamoh S, Hashimoto M, Sugioka K, et al. Chronic administration of docosahexaenoic acid improves reference memory-related learning ability in young rats. Neuroscience. 1999;93(1):237-41.
(7) McCann JC, Ames BN. Is docosahexaenoic acid, an omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid, required for development of normal brain function? An overview of evidence from cognitive and behavioral tests in humans and animals. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005 Aug;82(2):281-95.
(8) Dijck-Brouwer DA, Hadders-Algra M, Bouwstra H, et al. Lower fetal status of docosahexaenoic acid, arachidonic acid and essential fatty acids is associated with less favorable neonatal neurological condition. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2005 Jan;72(1):21-8.
(9) Kris-Etherton PM, Taylor DS, Yu-Poth S, et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acids in the food chain in the United States. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000 Jan;71(1 Suppl):179S-88S.
(10) Lorente-Cebrián S, Costa AG, Navas-Carretero S, Zabala M, Martínez JA, Moreno-Aliaga MJ. Role of omega-3 fatty acids in obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular diseases: a review of the evidence. J Physiol Biochem. 2013. Jun 22
(11) Unpublished, internal data. Ingenutra.
(12) Fortin S, inventor; Centre de Recherche sur les Biotechnologies Marines, assignee. Compositions comprising polyunsaturated fatty acid monoglycerides or derivatives thereof and uses thereof. US patent 8,198,324. June 12, 2012.
(13) Brunet S, Chamoun R, Fortin S, et al. MaxSimil®: A novel, patented natural platform for enhanced absorption of omega-3s. Single dose, double-blind, 2-way crossover pilot pharmacokinetic study on healthy subjects under normal diet. Sherbrooke (Québec), Canada: Ingenutra; 2018. [Unpublished]





Comments
Thank you Zach.
I met Zach at our local fresh food market about a week ago. Zach was busy but stopped what he was doing to spend some time educating me on proper nutrition and specifics in regard to meeting my goals. Appreciate you spending the time with me. I look forward to being healthier.
Awesome, Randy!
Zach knows his stuff!
Dr Perlmutter apparently had been looking through the data on the BlueZone cultures [ those people are not only more likely to pass 90 years old — over 30% likely — but they are vigorously healthy -vs- a dozen prescriptions and decrepit like in western medicine land] … Perlmutter commented that the average intake of olive oil [evo] was an astounding PINT PER WEEK PER PERSON… that’s about 1oz/meal x2meals per day… and that would amount to a LOT of omega 3… about 400mg/day [courtesy of wikipedia]…. the rest of their diet was lots of veggies and fish, [other meat varied by locale] whether they were mediteranean, central american, or far east… and to cap off the commonalities, i’ll point out — since no one else will — that they all lived in climates that were under 1000 heating degree days per year, even the 7th Day Adventists are predominately southern USA…. not like Ohio’s 5000 HDD per year.. so who knows how many oz/day you’d need in northern climates… more fuel needed in the cold, just ask any stray cat in our naturopathic rescue work, lol… ttyl
You’re awesome, MJ! As always, thank you for your brilliant contributions!